Product Code : 3D-TiNbMo-CU-PO5
TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy (HEA) Spherical Powder is a new type of alloy, which is very unique in performance. The different sizes and binding forces between the elements cause the alloy to have lattice distortion and slow diffusion effects. The current research shows that TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy (HEA) Spherical Powder is excellent in mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance, magnetic properties, and radiation resistance, and low-temperature properties.
Please contact us if you need customized services. We will contact you with the price and availability in 24 hours.
| Product | Product Code | Purity | Size | Contact Us |
Product Information
TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy (HEA) Spherical Powder is a new type of alloy, which is very unique in performance. The different sizes and binding forces between the elements cause the alloy to have lattice distortion and slow diffusion effects. The current research shows that TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy (HEA) Spherical Powder is excellent in mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance, magnetic properties, and radiation resistance, and low-temperature properties.
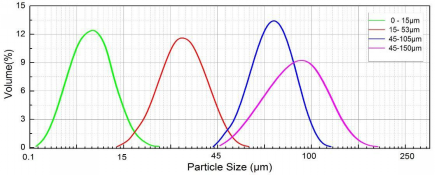
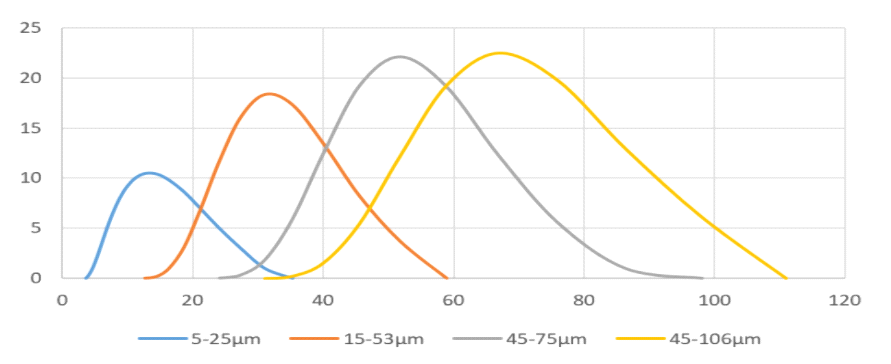
TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloys Spherical Powder Particle Size
0-45um,0-53um,15-45um, 15-53um, 45-105um (Various granularities can be customized according to customer requirements)
TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloys Spherical Powder Application
TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy (HEA) Spherical Powder is widely used in aerospace parts and auto parts, profile surface coating, powder metallurgy, nuclear energy and industrial fields.
High-Entropy Alloys Manufacture
High-entropy alloys are difficult to manufacture using extant techniques , and typically require both expensive materials and specialty processing techniques. High-entropy alloys are mostly produced using methods that depend on the metals phase – if the metals are combined while in a liquid, solid, or gas state. Most HEAs have been produced using liquid-phase methods include arc melting, induction melting, and Bridgman solidification. Solid-state processing is generally done by mechanical alloying using a high-energy ball mill. This method produces powders that can then be processed using conventional powder metallurgy methods or spark plasma sintering. This method allows for alloys to be produced that would be difficult or impossible to produce using casting, such as AlLiMgScTi. Gas-phase processing includes processes such as sputtering or molecular beam epitaxy (MBE), which can be used to carefully control different elemental compositions to get high-entropy metallic or ceramic films. Additive manufacturing, can produce alloys with a different microstructure, potentially increasing strength (to 1.3 gigapascals) as well as increasing ductility. Other techniques include thermal spray, laser cladding, and electrodeposition.
TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy Spherical Powder Particle Size Description
· 0-15μm (D10=3~5μm, D50=6~10μm, D90=12~14μm)
· 5-25μm (D10=5~10μm, D50=15~20μm, D90=20~25μm)
· 15-45μm (D10=15~20μm,D50=25~30μm,D90=35~40μm)
· 15-53μm (D10=15~20μm,D50=25~35μm,D90=45~50μm)
· 45-75μm (D10=45~55μm,D50=55~65μm,D90=70~75μm)
· 45-105μm (D10=50~60μm,D50=75~85μm,D90=95~105μm)
· 45-150μm (D10=55~70μm,D50=110~120μm,D90=140~150μm)
· 75-150μm (D10=80~90μm,D50=110~125μm,D90=135~150μm)
Packing of TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy Spherical Powder
Standard Packing:
Typical bulk packaging includes palletized plastic 5 gallon/25 kg. pails, fiber and steel drums to 1 ton super sacks in full container (FCL) or truck load (T/L) quantities. Research and sample quantities and hygroscopic, oxidizing or other air sensitive materials may be packaged under argon or vacuum. Solutions are packaged in polypropylene, plastic or glass jars up to palletized 440 gallon liquid totes Special package is available on request.
ATTs’TiNbMoTaW High-Entropy Alloy Spherical Powder is carefully handled to minimize damage during storage and transportation and to preserve the quality of our products in their original condition.
High-Entropy Alloys Species
| FeCoNiCr | NbMoTaW |
| CoCrFeNiMn | TiZrHfNbMo |
| AlCrFeCoNi | TiZrHfVMo |
| AlCoCrFeNi | TiZrVNbMo |
| FeMnCoCr | ZrVMoHfNb |
| TiZrHfVNb | WMoTaZr |
| TiNbMoTaW | TiZrTaMoNb |
| CuAlTiWV | CuAlTiVW |
| CoCrFeNiMo | NbMoTaWAl |
| TiVAlCrZr | TiZrVTa |
| FeNiCrCuAl | FeCoNi(AlSi)0.2 |
| CoCrFeNiV | Al1Mo0.5Nb1Ta0.5Ti1Zr1 |
| AlZrNbMo | Al4TiVFeSc |
| CrMnFeCoNi | Al4TiVFeGe |
| CoCrNiAl | Al4TiVFeCr |
| CoCrFeNiCu | CoCrFeNiTi |
| CoCrFeNiAl | CoCrFeNiCu |
| ZrMoCrNb | CoCrFeNiMo |
| TaHfZrTi | CoCrNiAlTi |
| AlCrFeCuNi | FeCrCoAlTi |
| AlFeNiCoCr | TiZrVTaMo |
| TiZrHfVTa | ZrTiHfNbMo |
| High-entropy Alloy Powder List | |
| Al0.5CoCrFeNi Powder | AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Powder |
| Al1.8CrCuFeNi2 Powder | NbMoTaW Powder |
| Al0.5CoCrFeNi Powder | NbMoTaWAl Powder |
| Fe50Mn30Co10Cr10 Powder | TiZrVTa Powder |
| FeCoNiCrAl Powder | FeCoNi(AlSi)0.2 Powder |
| CrMnFeCoNi Powder | Al1Mo0.5Nb1Ta0.5Ti1Zr1 Powder |
| Al4TiVFeSc Powder | CrFeCoNi Powder |
| Al4TiVFeGe Powder | CoCrNi Powder |
| Al4TiVFeCr Powder | CoCrFeNiMn Powder |
| NbMoTaWV Powder | CoCrFeNiMo Powder |
| AlCoCrFeNi Powder | |